Abstract
Objective: Staging of multiple myeloma(MM) patients at diagnosis predicts survival but the utility of applying them to restaging at disease progression has not been fully explored. Here, we investigate the prognostic impact of dynamic assessment of risk stratification.
Methods: We conducted this retrospective study to evaluate the prognostic impacts of staging and restaging among 263 newly diagnosed -progression paired patients diagnosed between 24 March 2013 and 2 December 2019. Currently used ISS and RISS were applied for dynamic assessment of risk stratification both at diagnosis and progression.
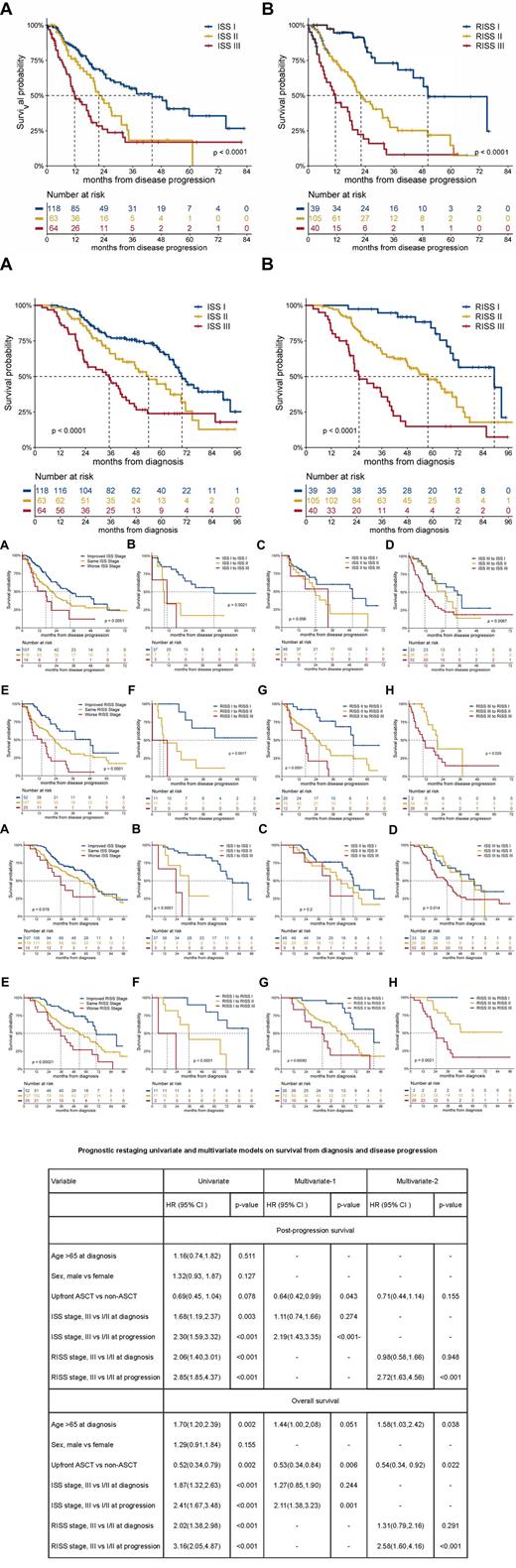
Results: 263 and 257 patients had Staging data for ISS and RISS at diagnosis while 245 and 184 patients were available for ISS and RISS restaging at progression .By restaging the ISS at progression, the median post-progression survival of patients of stage I, II, III was 44.2, 21.7 and 11.6 months, respectively (P﹤0.0001) and the median overall survival (mOS) was 69.8, 53.9 and 35.2 months in patients who stage had I, II, III disease, respectively (P﹤0.001). By restaging the RISS at progression, the median post-progression survival of stage I,II,III was 50.3, 22.2 and 11.4 months, respectively(P﹤0.0001), the mOS of stage I, II, III was 89.3,57.8 and 25.2 months in patients who stage had I, II, III disease, respectively (P﹤0.001). Among patients with available data on staging and restaging, migrated to advanced ISS/RISS stages or maintained ISS/RISS III disease at progression associated with dismal post-progression survival and OS. Multivariate analysis showed that the stage at the time of progression was independent of stage at diagnosis and first line ASCT and was an independent poor prognostic factor for post-progression survival and OS.
Conclusion: It is feasible for risk stratification reassessment at progression by using ISS and RISS. The prognostic significance of restaging at progression can overcome the prognostic value of staging at diagnosis, patients who migrated to higher stage predicts poor prognosis.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.